Deformable Particle Model (DPM)
Contents
DPM Theory
Deformable particles change shape in response to internal and external forces, as shown in Figure 1. To represent the shape of a deformable particle, many degrees of freedom are needed. In two dimensions, we use a discreet parametric representation of an Ns-sided polygon, where 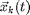 , is the k-th vertex position.
, is the k-th vertex position.
D0=0.4817; x=[-0.8523 -1.3274 -1.7837 -2.1240 -2.2230 -1.9576 -1.5714 -1.2077 -0.8314 -0.3904 0.0639 0.5030 0.9055 1.2836 1.6421 1.9462 2.1098 2.0278 1.6983 1.2585 0.8124 0.4025 0.0150 -0.3997]'; y=[-0.4840 -0.4992 -0.4362 -0.1670 0.2211 0.5499 0.8036 1.0775 1.3177 1.4183 1.3533 1.1594 0.8755 0.5502 0.2010 -0.1922 -0.6450 -1.0864 -1.3155 -1.2957 -1.1630 -0.9508 -0.7310 -0.5615]';
Files
- DeformableParticleModel.m Description of DPM. (This File)
- DeformableParticleModel.pdf PDF version.
- md010.m Simple molecular dynamics simulation with comments.
- dpm000.m Example DPM code with comments.
- dpm001.m DPM code with movie output.
- calcExtHull.m Support file for DPM visualization.
- ppack.m Support file for creating initial conditions for DPM.
- dpm.mp4 Movie of DPM simulation.
- DeformableParticleModel.zip All files in one zip file.
